students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory|Solved: Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic : warehouse Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares . Resultado da O grupo . MAXXSLOT. é uma das mais renomadas empresas internacionais de operação de cassino online, oferecendo uma ampla variedade de jogos empolgantes, como jogos ao vivo com crupiê real, slots, pesca, loterias, esportes e muito mais.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Aniversário Agosto 9, 1994. Signo Leão. Local de Nascimento , Idade 29 anos de idade. #2488 Mais Popular. Impulsionar. Sobre. Influenciadora digital e .
ap bio unit 7 Flashcards
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree.Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a .Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a .
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares .
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares .
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the 2 points laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a .Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a .Although all organisms carry out some form of cellular respiration, only certain organisms, called photoautotrophs, can perform photosynthesis. Examples of photoautotrophs include plants, algae, some unicellular eukaryotes, and .
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a .
Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. AP Biology Test Booklet Ch. 3: Origin and History of Life Name 1. Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms .
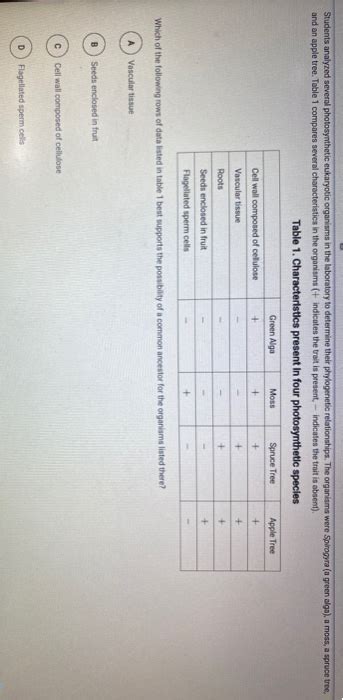
Try the fastest way to create flashcards. hello quizlet. HomeStudents analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares several characteristics in the organisms (+ indicates the trait is present, − indicates the trait is absent .Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares several characteristics in the organisms (+ indicates the trait is present, − indicates the trait is absent . Introduction. The evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis changed the world. The build-up of atmospheric oxygen that started around 2.7 billion years ago was largely due to the ability of cyanobacteria to extract electrons from water (releasing molecular oxygen) with the help of two photosystems linked in series (Holland, 2006; Farquhar et al., 2010). .
Some organisms are capable of capturing the energy from sunlight and using it to produce organic compounds. This process, known as photosynthesis, is essential to life as it provides energy for both producers and consumers.Photosynthetic organisms, also known as photoautotrophs, are organisms that are capable of photosynthesis.82% of students achieve A’s after using Learn. Study with Learn. Students also studied. Oral Pathology - Week 1 - Chapter 1 . Match the name of the eukaryotic organism with its description. Helminth- multicellular animals Algae- unicellular or multicellular photosynthetic protists Filamentous fungi- multicellular, cell walls of chitin, .
Solved: Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What are the reactants for photosynthesis?, What organelle, present in eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms, is the location of photosynthesis?, During photosynthesis, where .Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory from SCIENCE AP BIO at Syosset High School. AI Homework Help. Expert Help. Study Resources. Log in Join. Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic. Doc Preview. Pages 13. Identified Q&As 26. Syosset High School. SCIENCE. SCIENCE AP BIO.Photosynthetic Structures in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes. In all phototrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside a chloroplast, an organelle that arose in eukaryotes by endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic bacterium (see Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells).These chloroplasts are enclosed by a double membrane with inner and outer layers.Photosynthesis changes sunlight into chemical energy, splits water to liberate O 2, and fixes CO 2 into sugar.. Most photosynthetic organisms are photoautotrophs, which means that they are able to synthesize food directly from carbon dioxide and water using energy from light. However, not all organisms use carbon dioxide as a source of carbon atoms to carry out .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Please select characteristics exhibited by prokaryotes to test your understanding of the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms., Complete each important historical foundations of microbiology sentence., Match each description to the correct group of microorganisms. and more.
This process involves a eukaryotic host cell engulfing a photosynthetic eukaryotic cell. The primary examples of such organisms are: . inner membrane, and thylakoid system. A chloroplast’s structure is complex, comprising several distinct components: Outer Membrane: The outer membrane is a semi-permeable barrier that encases the organelle. The occurrence of multicellular eukaryotes in Paleoproterozoic rocks not much younger than those containing the oldest unambiguous evidence of eukaryotes as a whole supports the hypothesis that simple multicellularity arose early in eukaryotic history, as much as a billion years before complex multicellular organisms diversified in the oceans.All other organisms are eukaryotes. The prefix “eu”- means “true.” The cells of eukaryotes have true, double-membrane nuclei containing their genetic material (DNA). Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in several ways. Eukaryotic .Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the 2 points laboratory to determine their phylogenetic relationships. The organisms were Spirogyra (a green alga), a moss, a spruce tree, and an apple tree. Table 1 compares several characteristics in the organisms ( + indicates the trait is present, - indicates the trait is absent).
In all autotrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside an organelle called a chloroplast. In plants, chloroplast-containing cells exist in the mesophyll. Chloroplasts have a double (inner and outer) membrane. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked, disc-shaped structures called thylakoids.Students also studied. lab quiz 3/22. 18 terms. mickayla_ng14. Preview. Green Algae and Land Plants . A _____ is a eukaryotic organism that is not a plant, animal, or fungus. . As new information is discovered and analyzed, the eukaryotic Kingdom _____ is being reevaluated by taxonomists because it consists of about 100,000 greatly varied .
Students also viewed. AP Biology Unit 4 Hager (MC & FRQ) 32 terms. Iambingo. . Besides being photosynthetic eukaryotes, what other traits do green algae share with modern landplants? . what does the pattern of organisms that are capable of photosynthesis indicate about its possible origin in these groups? - It is likely to have evolved .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Genetic Material for Viruses, Genetic Material for Viroids, Genetic Material for Prions and more.Cells are divided into two main classes, initially defined by whether they contain a nucleus. Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) lack a nuclear envelope; eukaryotic cells have a nucleus in which the genetic material is separated from the cytoplasm. Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells; in addition to the absence of a nucleus, their genomes are less .
6. Kingdom ----- consists of multicellular eukaryotes that produce their food by photosynthesis. 7. Kingdom -----includes eukaryotic organisms that mostly decompose organic wastes and absorb nutrients into their cells. 8. Kingdom ----- consists of multicellular eukaryotes that obtain their food by ingesting (eating) other organisms.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Protists contain clues of important evolutionary milestones in eukaryotic organisms, such as the origins of chloroplasts, mitochondria, and, In ________ endosymbiosis, an early eukaryotic organism engulfed a cyanobacterium, which became a chloroplast. In _______ endosymbiosis, one eukaryote .
Eukaryotes are extraordinarily keen on establishing symbiotic associations with other organisms. Leaving apart the mitochondrion, there is virtually no eukaryote lacking any form of symbiosis , and surprisingly common are instances of multiple, matrioshka-like associations (Douglas 2014).. Focusing on symbioses in which at least one of the symbionts is . These three groups of protists differ greatly in terms of their basic characteristics. For example, algae are photosynthetic organisms that can be unicellular or multicellular. Protozoa, on the other hand, are nonphotosynthetic, motile organisms that are always unicellular. Other informal terms may also be used to describe various groups of . Final answer: Eukaryotic algal cells are a good choice for monitoring both photosynthesis and cellular respiration because they contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria.These cells perform photosynthesis to manufacture their own food and produce oxygen, which is then used in cellular respiration to produce ATP. The ability to photosynthesize is found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms. The most well-known examples are plants, as all but a very few parasitic or mycoheterotrophic species contain chlorophyll and produce their own food. Algae are the other dominant group of eukaryotic photosynthetic organisms. All algae, which include massive .
web9 de out. de 2023 · Procuro garota pra um ERPG longo e desenvolvido de Ordem .
students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms in the laboratory|Solved: Students analyzed several photosynthetic eukaryotic